© 2025 MumbaiExclusive. All Rights Reserved.
Business
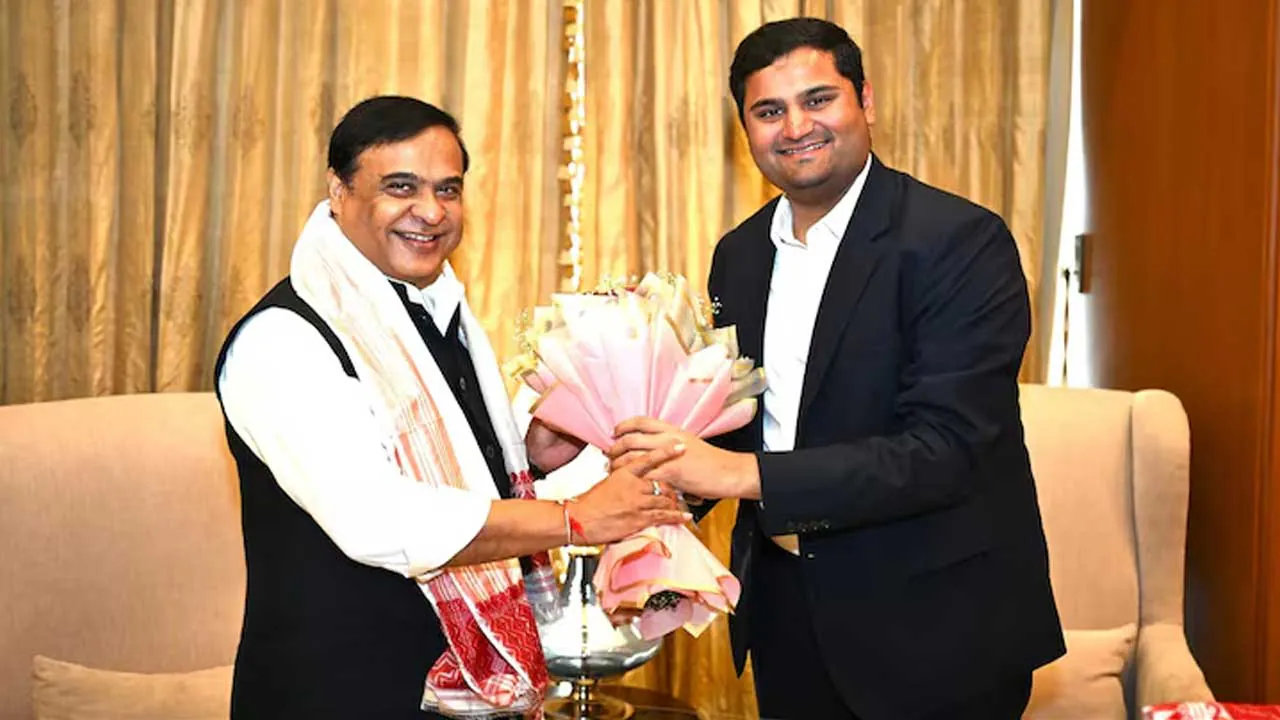
Himanta Sarma and Jeet Adani Talk About Assam’s Rs 50,000 Crore Investment Plan
Himanta Biswa Sarma, the chief minister of Assam, met with Jeet Adani, the director of the Adani Group, on Sunday to talk about the Rs…
Entrepreneur
Science
Can wrinkles be smoothed overnight with anti-aging creams? This is how they operate.
Anti-aging creams are only one of many products in the cosmetics business…
Reasons not to self-medicate
For many people who are experiencing emotional or physical discomfort, self-medication has…
What would happen if you squeezed your eye and got splashes of lemon juice in it?
A common kitchen or culinary mishap includes droplets splashing into one’s eye…
Will India’s medical equipment business be impacted by US tariffs? This is how to decipher the ripple effect.
Since the US is their biggest market and would account for 31.3%…
Sports
Lifestyle
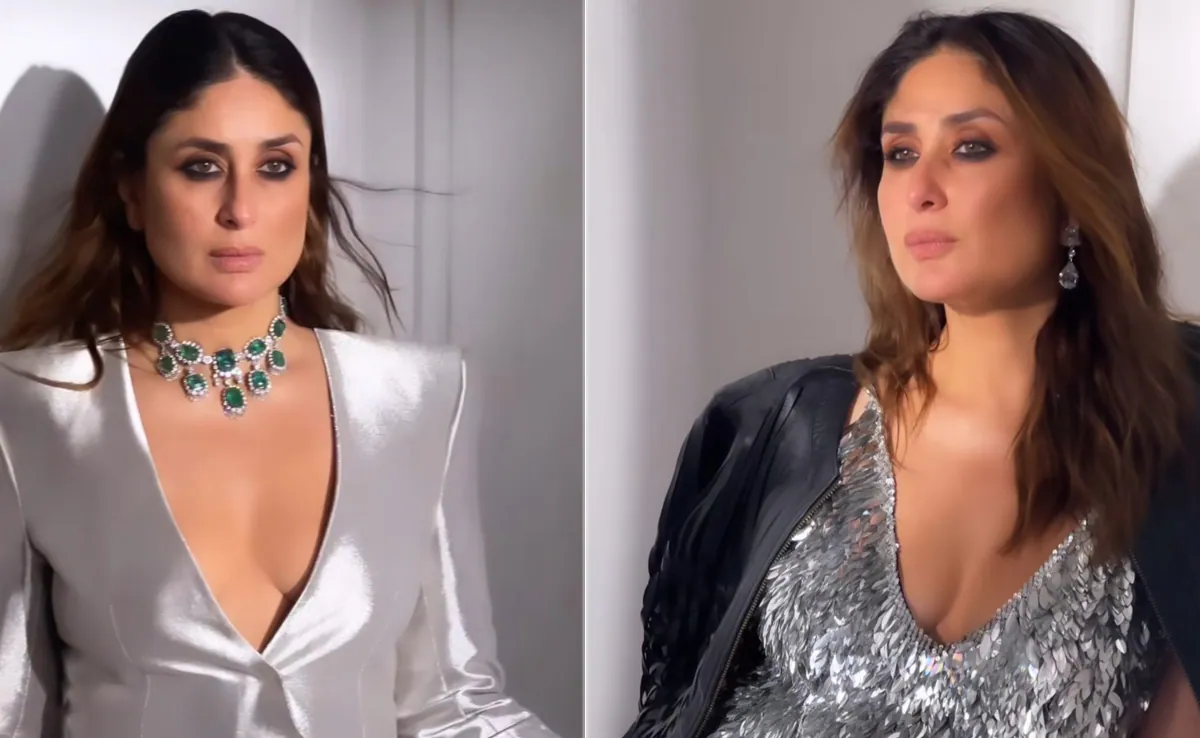
Caramel Lips and Smokey Kohl-Filled Eyes: Kareena Kapoor Is the Best at Selfies
In addition to being the queen bee of Bollywood, Kareena Kapoor has…
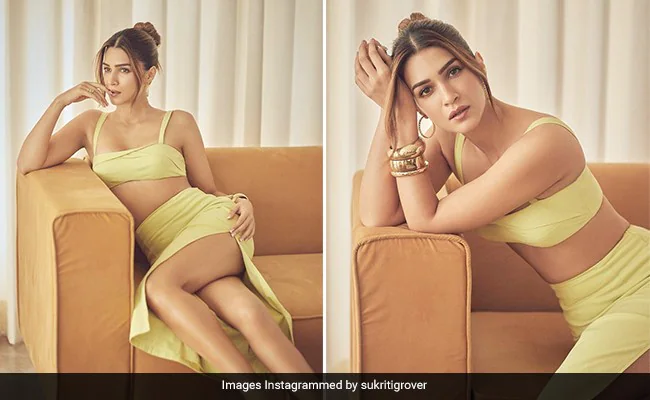
Kriti Sanon’s Peach-Perfect Glam and Radiant Complexion Work Like Magic
When Kriti Sanon adorned herself to appear on the most recent cover…
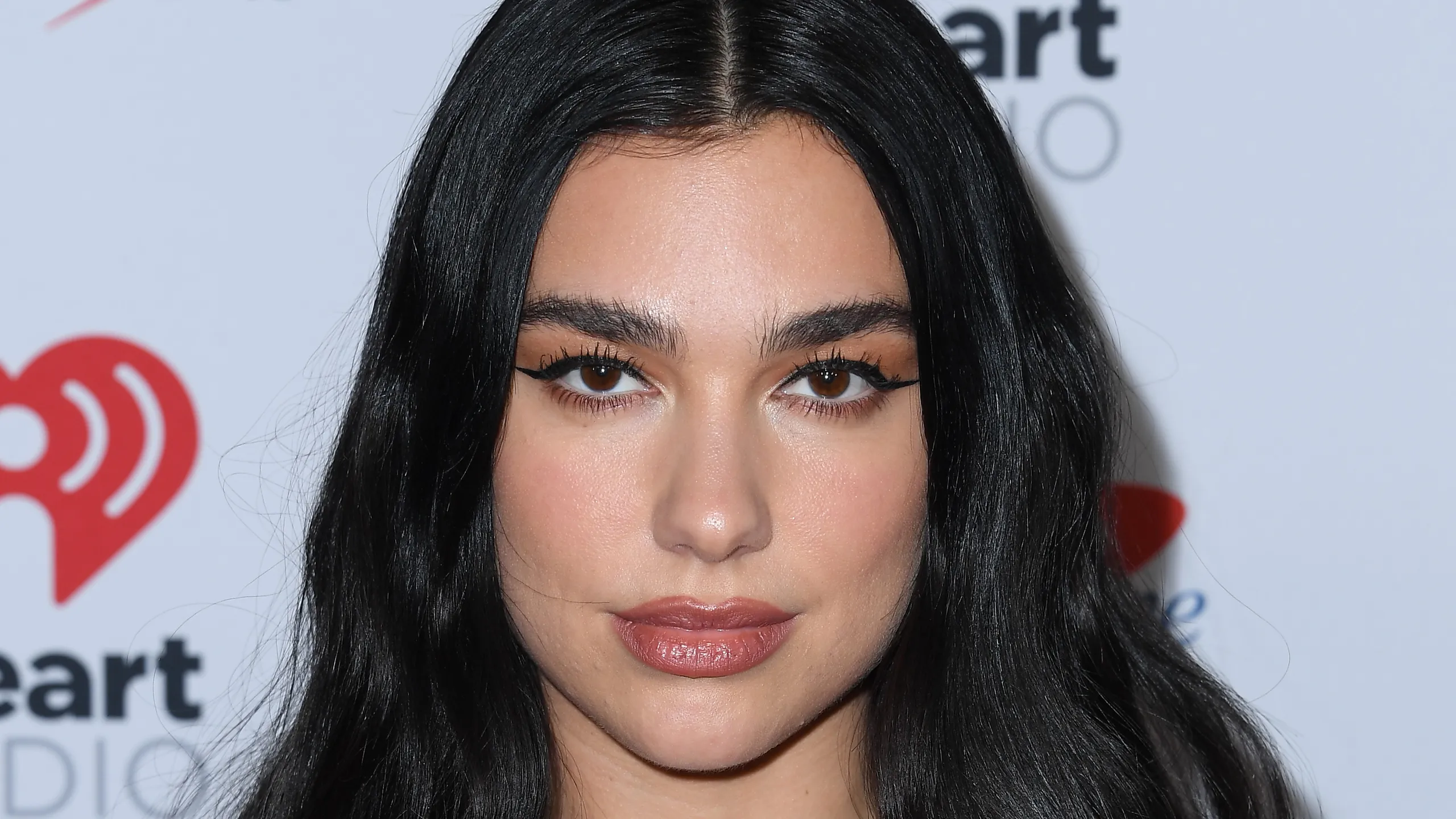
Save Dua Lipa’s Blushed Spring Glam to your bookmarks for the ideal petal-core makeup.
In her petal-like and flawless glam avatar, Albanian and English singer and…
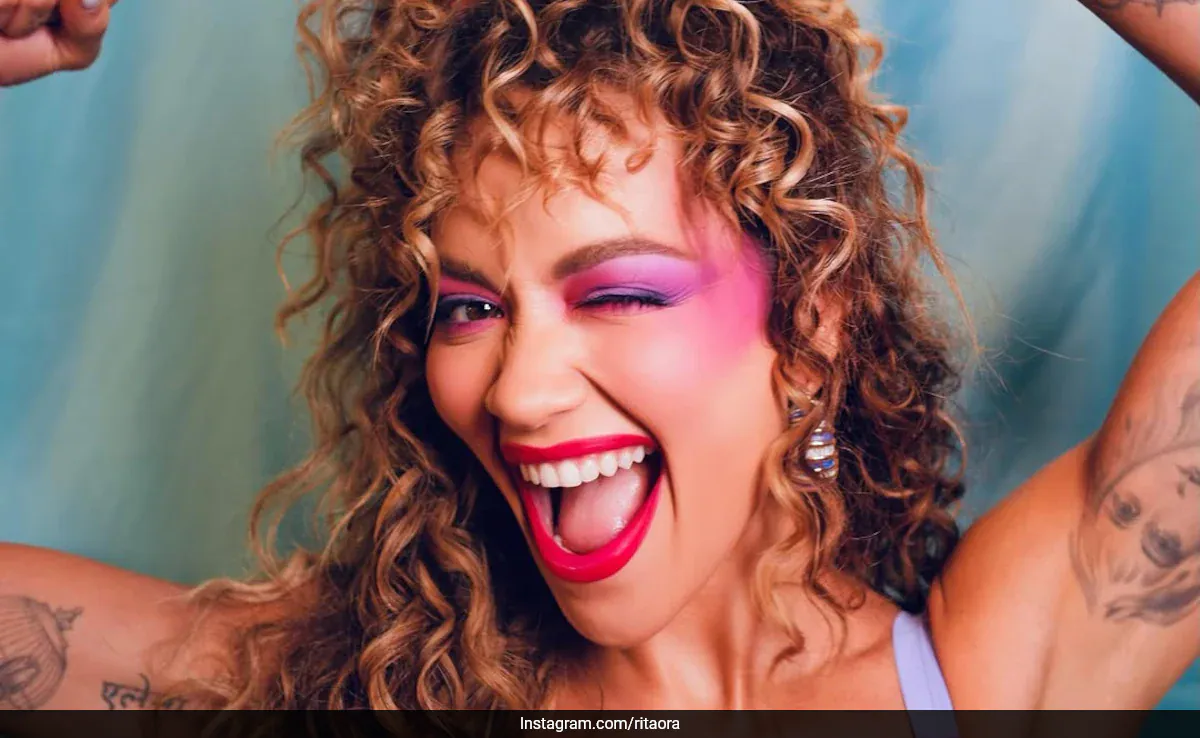
Rita Ora Receives a Glam Green Flag for Her Mauve Lips, Blushed Cheeks, and Sunset-Silver Eyes
Rita Ora, a British singer, appeared like a complete diva when she…